Page 41 - International safety guide for oil tankers and terminals
P. 41
BASIC PROPERTIES OF PETROLEUM
B
15 F
งานห้องสมุด ศูนย์ฝกพาณิชย์นาวี
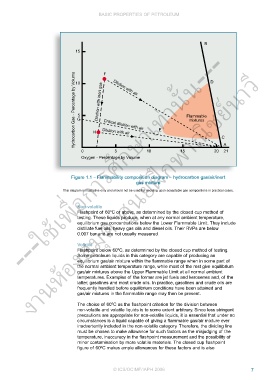
Hydrocarbon Gas - Percentage by Volume 10 Dilution with inert gas Critical dilution with air Eท่านั้น--- D
Dilution with air
---ใช้เพื่อการศึกษาเ
5
Flammable
G
mixtures
0 H Dilution with air 10 15 20 C A
5
21
Oxygen - Percentage by Volume
ึ
Figure 1.1 – Flammability composition diagram – hydrocarbon gas/air/inert
gas mixture
This diagram is illustrative only and should not be used for deciding upon acceptable gas compositions in practical cases.
Non-volatile
Flashpoint of 60ºC or above, as determined by the closed cup method of
testing. These liquids produce, when at any normal ambient temperature,
equilibrium gas concentrations below the Lower Flammable Limit. They include
distillate fuel oils, heavy gas oils and diesel oils. Their RVPs are below
0.007 bar and are not usually measured.
Volatile
Flashpoint below 60ºC, as determined by the closed cup method of testing.
Some petroleum liquids in this category are capable of producing an
equilibrium gas/air mixture within the flammable range when in some part of
the normal ambient temperature range, while most of the rest give equilibrium
gas/air mixtures above the Upper Flammable Limit at all normal ambient
temperatures. Examples of the former are jet fuels and kerosenes and, of the
latter, gasolines and most crude oils. In practice, gasolines and crude oils are
frequently handled before equilibrium conditions have been attained and
gas/air mixtures in the flammable range may then be present.
The choice of 60ºC as the flashpoint criterion for the division between
non-volatile and volatile liquids is to some extent arbitrary. Since less stringent
precautions are appropriate for non-volatile liquids, it is essential that under no
circumstances is a liquid capable of giving a flammable gas/air mixture ever
inadvertently included in the non-volatile category. Therefore, the dividing line
must be chosen to make allowance for such factors as the misjudging of the
temperature, inaccuracy in the flashpoint measurement and the possibility of
minor contamination by more volatile materials. The closed cup flashpoint
figure of 60ºC makes ample allowances for these factors and is also
© ICS/OCIMF/IAPH 2006 7